#均衡饮食
#系列课程
购物的重要作用
购物是确保您能够实现并保持健康均衡饮食的重要组成部分。定期购买健康食品非常重要,这样您才能随时掌握这些食物,避免不得不去快餐店和方便食品店。
选购食品的关键原则
- 列出你计划在下周饮食中包含的健康膳食和零食。制定膳食计划非常重要,这样你就可以一次性完成所有购物,从而节省时间。
- 使用这份健康膳食和零食清单创建购物清单。
- 定期购物,以便在需要时有最佳的食物选择。
- 只购买清单上的商品。这将减少购买不需要食物的可能性,从而帮助你保持健康饮食并省钱。
- 确保你在购物时不感到饥饿。你可能会更容易受到诱惑,购买那些方便但不健康的食物(脂肪、糖和卡路里含量较高)。
- 了解商店布局,以便快速而有目的地购物。你逛的时间越长,就越有可能做出不健康的食物选择。
- 尽量不要被不健康食品的特价商品所吸引。打折并不意味着它对你的健康有益。
- 避免诱惑。例如,如果您对烘焙食品情有独钟,千万要错过烘焙区。
- 阅读食品标签。食品标签上的信息可以帮助您做出最佳选择。更多信息,请参阅下方关于阅读标签的表格。
- 购物后回家,请立即将新鲜食品放入冰箱冷藏,将冷冻食品放入冷冻室。
购物时如何做出最佳食物选择
- 摄入大量新鲜水果和蔬菜
- 选择全谷物和高纤维食物
- 选择不饱和脂肪和油脂,例如牛油果、坚果、种子、橄榄油和菜籽油
- 选择优质蛋白质,例如去皮鸡肉、鸡蛋、鱼肉和瘦肉(去除多余脂肪)
- 选择脱脂或低脂牛奶和乳制品
- 避免食用精制淀粉类食物
- 远离含糖食物和饮料
- 尽量避免食用高脂肪、反式脂肪或饱和脂肪的食物,例如油炸食品、高脂肪食品、人造黄油、黄油、奶油、起酥油、猪油、馅饼、糕点和披萨。
阅读食品标签的提示和技巧
食品上的标签可以告诉您很多有关食品的信息。了解食品标签将有助于您在购物时做出明智的选择。下表 1 将帮助您更好地理解食品标签,此处提供的标签图片可用于识别表格中的内容。
标签示例
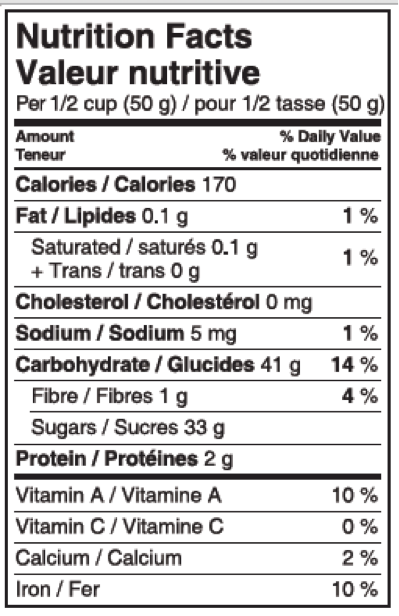
营养成分表
配料表 配料按重量降序排列。点击此处了解更多信息。建议避免购买含有大量不良成分的产品。
营养成分表 此处列出了食品中所含的营养成分。某些食品可能没有此标签,例如新鲜水果和蔬菜、店内烹制的食品以及小包装食品。点击此处查看食品标签上通常包含的营养成分列表。选择食品时,比较类似产品的标签很有用。例如,如果您将一种产品的饱和脂肪含量与类似产品的饱和脂肪含量进行比较,您将能够选择饱和脂肪含量最低的食品。其他营养成分也可以这样做。
食用份量 食用份量是指每人食用一份食物的量或计量单位。
卡路里 卡路里是用来测量产品所含能量的单位。标签上的总卡路里取决于产品中碳水化合物、蛋白质和脂肪的含量。
每日摄入量百分比 此百分比表示每份产品中的营养素含量与该特定营养素的每日推荐摄入量(通常基于每日2,000卡路里的饮食)的比率。例如:如果标签上注明该产品可提供您每日钙需求量的20%,则意味着您需要从其他食物来源获取剩余的80%钙需求(基于2,000卡路里饮食的合理假设)。
脂肪
饱和脂肪
反式脂肪
不饱和脂肪
饱和脂肪和反式脂肪非常有害,会增加患生活方式疾病的风险。食品标签上可能出现的高饱和脂肪成分包括奶油、黄油、可可脂和棕榈油。
不饱和脂肪更受欢迎,但由于脂肪能量密度高,因此也应控制其摄入量。不饱和脂肪的例子包括:菜籽油、橄榄油、牛油果、坚果、花生酱和种子。
胆固醇 胆固醇是一种脂质(脂肪的一种)。胆固醇摄入过高并不可取,因为它是导致心脏病的一个风险因素。
钠 钠指的是产品中的盐含量。摄入过多的钠可能会增加患高血压的风险。每日钠摄入量不应超过 2,400 毫克(毫克)。
维生素和矿物质 这会告诉你产品提供的维生素和矿物质占每日所需量的百分比。
购物时,请考虑您的健康和保健
您对食品和健康的了解越多,就越有可能持续选择健康的食物。购物时,请记住查看食品标签,并运用您在过去九周内学到的其他健康食品选择关键原则。购物有时可能感觉很麻烦,但如果您以健康和保健为中心,购物将是一项值得的练习。
本周重点信息
列出即将开始的正餐和零食清单,并以此为基础编制您的购物清单。购物时,尽量只购买清单上的商品。你可以运用本课讨论的技巧来帮助你,例如避免诱惑,避免在饥饿时购物。
确保你的购物清单包含大量新鲜水果、蔬菜、脱脂或低脂乳制品、不饱和脂肪和油脂、全谷物、高纤维食物以及富含蛋白质的健康食品,例如鱼、蛋、去皮鸡肉和瘦肉。
学会阅读和理解食品标签,因为这将有助于你在购物篮中添加食品时做出更明智的选择。
The important role of shopping
Shopping is an important part of ensuring that you are able to achieve and maintain a healthy balanced diet. It is important to regularly shop for healthy food so that you have these foods on hand and will not be put into the position of having to make use of fast-food outlets and convenience foods.
Some key principles on how to shop for food.
- Make a list of the healthy meals and snacks you intend to include in your diet over the next week. It is important to plan meals so that you can do all your shopping at once and save time overall.
- Create a shopping list using this list of healthy meals and snacks
- Shop regularly in order to have the best food choices on hand when you need them.
- Buy only the items on your list. This will reduce the likelihood of purchasing foods you do not need, which will help you maintain a healthy diet and save you money.
- Make sure you are not hungry when you go shopping. You may be more tempted to purchase foods that are convenient and less healthy (higher in fat, sugar, and calories).
- Know the shop layout well so that your shopping is quick and purposeful. The longer you wander, the more likely you are to make unhealthy food choices.
- Try not to be charmed by specials on unhealthy food items. Just because the food may be discounted does not mean it will be good for your health.
- Avoid temptation. For example, do not let yourself walk past the bakery section if baked goods are your temptation.
- Read food labels. Information found on food labels can assist you in making the best food choice. Refer to the table on reading labels below for more information.
- Head home after shopping and promptly place fresh items in the refrigerator and frozen items in the freezer.
Learn how to make the best food choices while shopping.
- Making the best food choices while shopping
- Here are some basic principles (from the past weeks’ lessons) to stick to when shopping for food:
- Include plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables
- Choose whole grain and high-fibre foods
- Choose unsaturated fats and oils, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive and canola oils
- Choose good quality protein choices such as skinless chicken, eggs, fish, and lean meat (that has been trimmed of excess fat)
- Choose fat-free or low-fat milk and dairy products
- Avoid refined starchy foods
- Stay away from sugary foods and beverages
- Try to avoid including foods high in fat, trans fat, or saturated fat, such as deep fried and fatty foods, brick margarines, butter, cream, shortening, lard, pies, pastries, and pizza.
Hints and tips for reading food labels
The labels that appear on food items can tell you a lot about the food. Understanding food labels will help you to make informed choices when shopping. Table 1 below will help you to understand food labels better, and the picture of a label given here can be used to identify what is being referred to in the table.
EXAMPLE LABEL

Nutrition facts
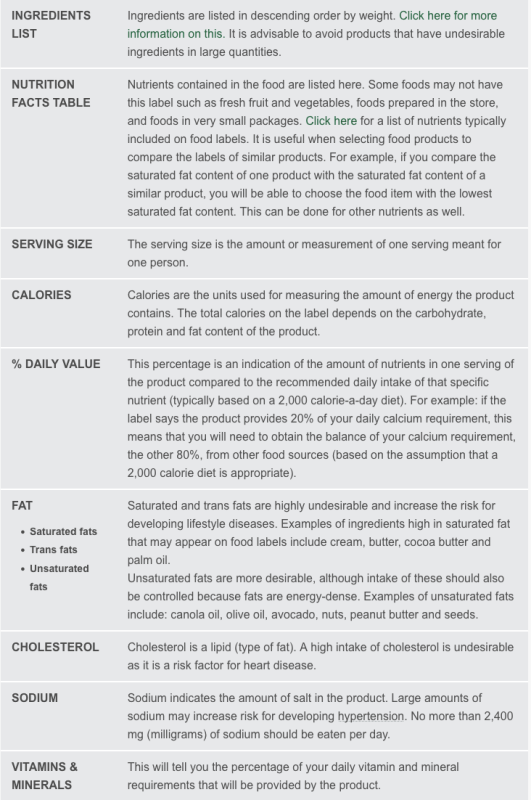
INGREDIENTS LIST Ingredients are listed in descending order by weight. Click here for more information on this. It is advisable to avoid products that have undesirable ingredients in large quantities.
NUTRITION FACTS TABLE Nutrients contained in the food are listed here. Some foods may not have this label such as fresh fruit and vegetables, foods prepared in the store, and foods in very small packages. Click here for a list of nutrients typically included on food labels. It is useful when selecting food products to compare the labels of similar products. For example, if you compare the saturated fat content of one product with the saturated fat content of a similar product, you will be able to choose the food item with the lowest saturated fat content. This can be done for other nutrients as well.
SERVING SIZE The serving size is the amount or measurement of one serving meant for one person.
CALORIES Calories are the units used for measuring the amount of energy the product contains. The total calories on the label depends on the carbohydrate, protein and fat content of the product.
% DAILY VALUE This percentage is an indication of the amount of nutrients in one serving of the product compared to the recommended daily intake of that specific nutrient (typically based on a 2,000 calorie-a-day diet). For example: if the label says the product provides 20% of your daily calcium requirement, this means that you will need to obtain the balance of your calcium requirement, the other 80%, from other food sources (based on the assumption that a 2,000 calorie diet is appropriate).
FAT
Saturated fats
Trans fats
Unsaturated fats
Saturated and trans fats are highly undesirable and increase the risk for developing lifestyle diseases. Examples of ingredients high in saturated fat that may appear on food labels include cream, butter, cocoa butter and palm oil.
Unsaturated fats are more desirable, although intake of these should also be controlled because fats are energy-dense. Examples of unsaturated fats include: canola oil, olive oil, avocado, nuts, peanut butter and seeds.
CHOLESTEROL Cholesterol is a lipid (type of fat). A high intake of cholesterol is undesirable as it is a risk factor for heart disease.
SODIUM Sodium indicates the amount of salt in the product. Large amounts of sodium may increase risk for developing hypertension. No more than 2,400 mg (milligrams) of sodium should be eaten per day.
VITAMINS & MINERALS This will tell you the percentage of your daily vitamin and mineral requirements that will be provided by the product.
Shop with your health and wellness in mind
The more knowledgeable you become about food and health, the more likely you are to consistently make healthy food choices. While shopping, remember to review food labels and apply the other key principles you have learned over the past nine weeks for healthy food selection. Shopping may feel like a chore at times, but it is a worthwhile exercise if you complete it with your health and wellness in mind.
Key messages for this week
Create a list of upcoming meals and snacks and use it to compile your shopping list. When shopping, try to only purchase items on your list. You can utilize the techniques discussed in this lesson to help you, such as avoiding temptation and not shopping while hungry.
Ensure that your shopping list includes plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables, fat-free or low-fat dairy products, unsaturated fats and oils, whole grain, high-fibre foods, and healthy protein-rich foods, such as fish, eggs, skinless chicken and lean meat.
Learn to read and understand food labels, as it will help you to make more informed choices about the food you add to your shopping basket.